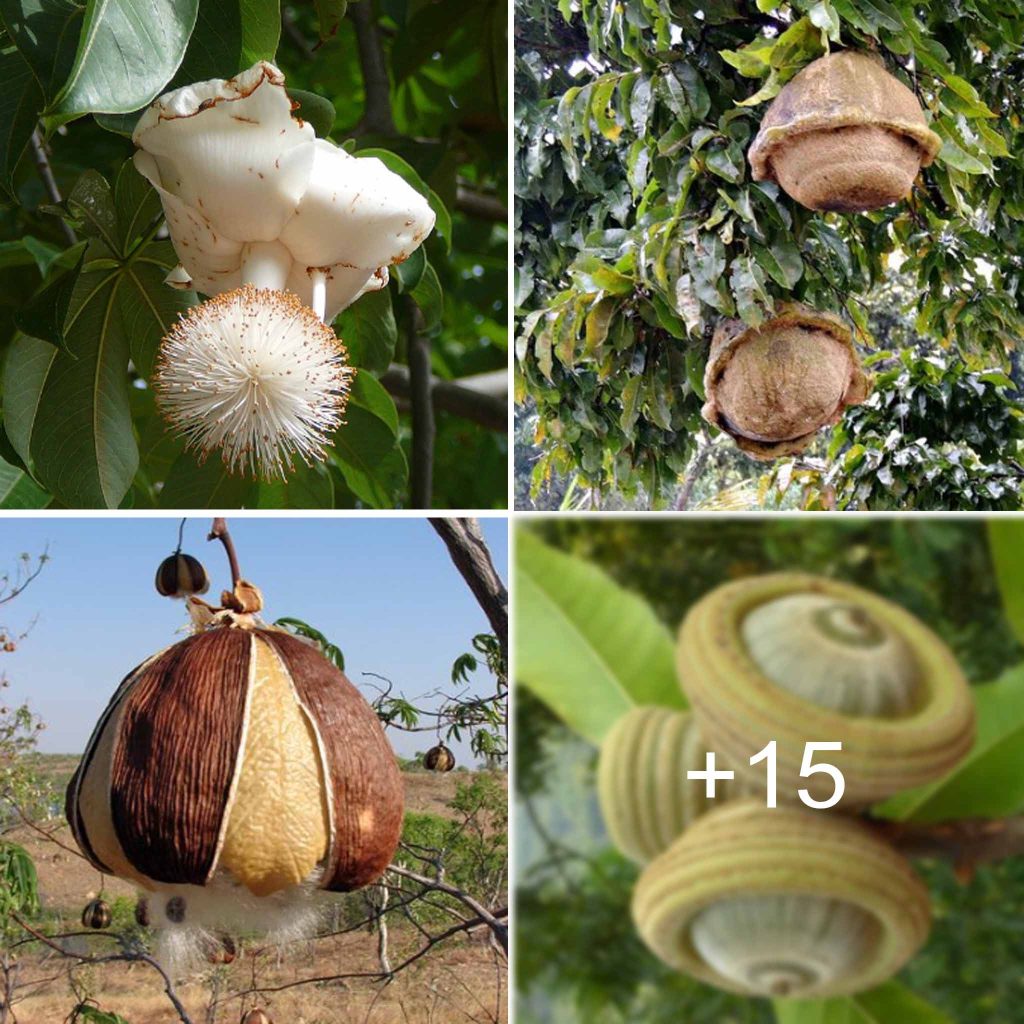
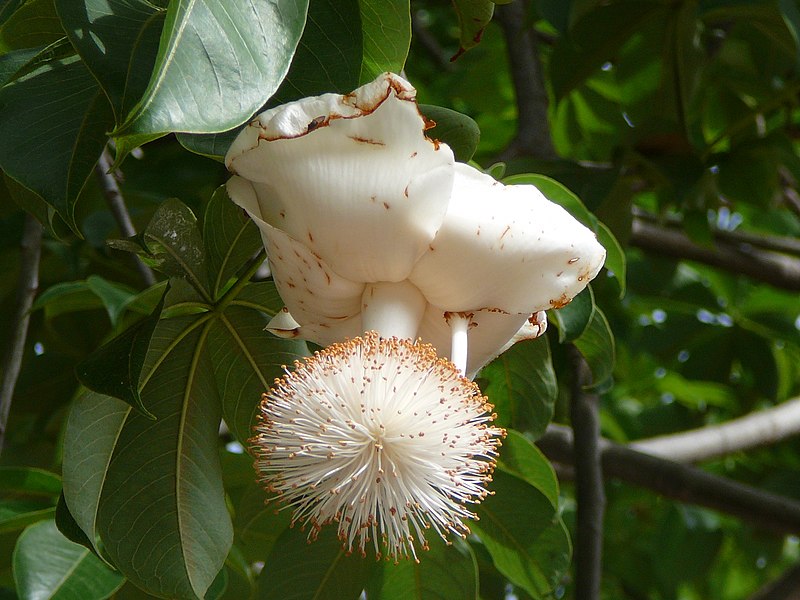
Medicinal plants have been used for centuries in traditional medicine systems around the world, providing natural remedies for various ailments. Understanding the development process of these valuable plants is essential to harness their healing potential. This article delves into the intricate journey of the development of medicinal plants, from cultivation to use.
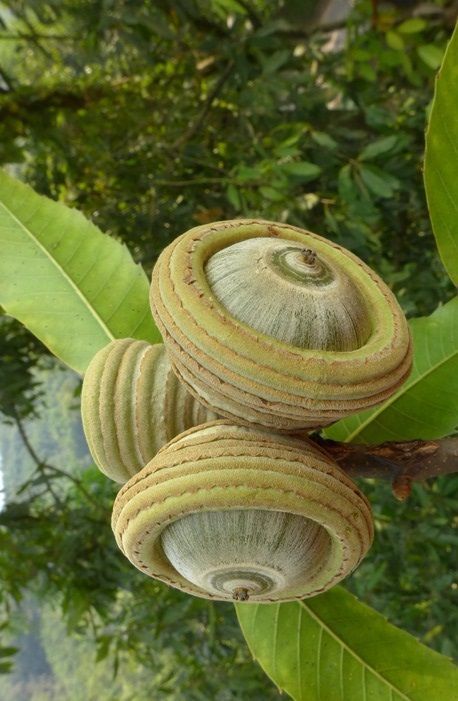

- Selection of medicinal plant species: The first step in the development process is the careful selection of plant species with known medicinal properties. These selections are usually based on historical use, traditional knowledge, or scientific research.

- Cultivation and propagation: Medicinal plants can be grown in the wild or in controlled environments. Growing methods vary depending on plant species, climate and region. Propagation techniques such as seeds, cuttings or tissue culture are used to ensure the availability of a constant and healthy supply of plants.
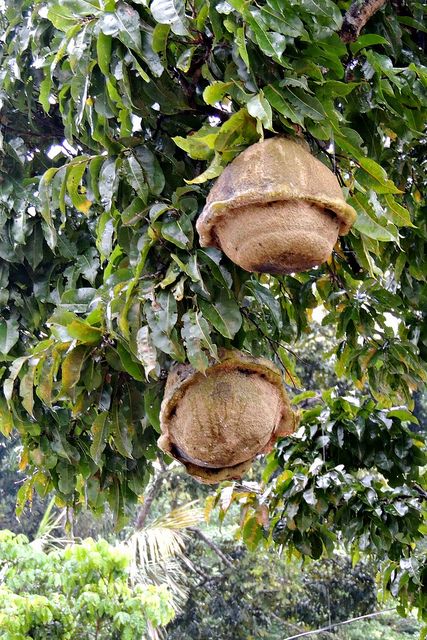

- Soil Preparation and Growing Conditions: Proper soil preparation and maintaining optimal growing conditions, including sunlight, temperature and humidity, are crucial to the successful cultivation of medicinal plants. Organic farming practices are often preferred to minimize the presence of contaminants.
- Harvest: The timing of harvest is essential as it directly affects the potency of the plant. Medicinal plants are typically harvested during specific growth stages, when their bioactive compounds are most concentrated. Careful handling and processing methods are used to preserve the medicinal qualities of the plant.
- Drying and Preservation: After harvesting, medicinal plants are dried using various techniques such as air drying, sun drying or freeze drying. Proper drying ensures the preservation of the active compounds and prevents mold or decomposition. Once dried, the plants are stored in airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
- Quality Control and Testing: Medicinal plant products undergo rigorous quality control and testing procedures to verify their safety, potency and purity. This involves chemical analysis, microbial testing, and sometimes even genetic fingerprinting to ensure product consistency.
- Processing and formulation: Medicinal plants are processed into various forms, including powders, extracts, tinctures and capsules, depending on the intended use. Herbalists and manufacturers carefully formulate these products to maximize their therapeutic benefits.
- Regulatory compliance: In many countries, medicinal plant products are subject to regulatory oversight to ensure they meet safety and quality standards. Compliance with regulations is crucial for market access and consumer confidence.
- Research and innovation: Continuous research is vital to discover new species of medicinal plants, optimize cultivation techniques and identify new therapeutic applications. Scientific advances continue to expand our understanding of these valuable resources.